Key Factors for Low Voltage Switchgear Testing
Introduction
In electrical distribution systems, low voltage (LV) switchgear plays a crucial role in controlling, protecting, and isolating electrical equipment. To ensure safety, reliability, and compliance with industry standards, regular switchgear testing is essential. This article outlines the key factors to consider when testing LV switchgear to maintain optimal performance and prevent failures.
1. Insulation Resistance Testing
Insulation degradation over time can lead to electrical faults, short circuits, or fire hazards. Factors such as aging, environmental exposure, and electrical stress can compromise insulation integrity.
The insulation resistance test applies a high DC voltage to measure resistance values. A high insulation resistance indicates good insulation quality, while lower values suggest potential issues requiring maintenance. This test helps prevent leakage currents that could affect system performance.
2. Contact Resistance Testing
Electrical contacts in LV switchgear must maintain low resistance to ensure efficient power transfer. Over time, oxidation, corrosion, and wear can increase contact resistance, leading to:
- Voltage drops
- Excessive heating
- Energy losses
Contact resistance testing is performed by applying a known current through the closed contacts and measuring the voltage drop. If the resistance is too high, corrective actions such as cleaning, tightening, or replacing contacts may be required to prevent failures.
3. Visual Inspection and Mechanical Checks
Besides electrical tests, visual and mechanical inspections are critical to identifying physical wear and potential failures. These checks include:
- Inspecting busbars, circuit breakers, and enclosures for corrosion or damage.
- Ensuring proper alignment of components.
- Verifying the functionality of mechanical parts such as hinges, latches, and interlocks.
Routine inspections help detect early signs of deterioration and ensure that the switchgear remains fully operational.
4. Functionality Testing of Circuit Breakers
Circuit breakers in low voltage switchgear are responsible for protecting electrical systems from overloads and short circuits. Proper functionality testing ensures they operate correctly during fault conditions.
Testing includes:
- Primary injection testing to verify performance under load conditions.
- Trip setting verification to ensure proper operation.
- Mechanical and electrical operation tests to check breaker response time.
By simulating fault conditions, engineers can confirm that circuit breakers trip within the required time limits, ensuring the protection of both equipment and personnel.
5. Thermal Imaging and Temperature Monitoring
Excessive heat within LV switchgear is often a sign of loose connections, overloaded circuits, or failing components. Thermal imaging provides a non-invasive method to detect hot spots before they lead to major failures.
Benefits of thermal imaging testing include:
- Early detection of overheating components.
- Prevention of energy losses due to high resistance connections.
- Increased system reliability through proactive maintenance.
By identifying abnormal temperature variations, engineers can address potential failures before they cause unplanned downtime.
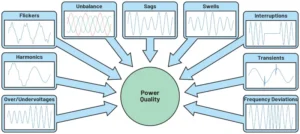
6. Power Quality Testing
Maintaining power quality is essential for efficient power distribution. Poor switchgear performance can lead to issues such as:
- Voltage sags or surges
- Harmonic distortions
- Unstable frequency levels
Power quality testing helps ensure smooth power distribution and minimizes risks associated with electrical imbalances. Key assessments include:
- Harmonic analysis
- Voltage regulation monitoring
- Power factor measurements
Regular testing improves energy efficiency and reduces the risk of equipment damage due to power fluctuations.
7. Tightness Test
Loose electrical connections can cause resistance buildup, leading to overheating, energy losses, and potential failures. The tightness test involves verifying the torque levels of all fasteners within the switchgear assembly.
This process ensures that:
- Busbar connections remain secure.
- Cable lugs and terminal blocks are properly fastened.
- Manufacturer-recommended torque values are met.
By conducting routine tightness tests, engineers can prevent issues related to mechanical loosening, ensuring long-term durability.
8. Compliance with Industry Standards
To ensure safety and reliability, low voltage switchgear testing must comply with industry regulations. Key standards include:
- IEC 61439 – Governing low voltage switchgear assemblies.
- IEEE C37.20 – Performance requirements for switchgear.
- NFPA 70E – Electrical safety regulations.
Following these standards guarantees that switchgear installations meet regulatory requirements and operate safely under various conditions.
Conclusion
Regular low voltage switchgear testing is essential for ensuring system reliability, efficiency, and compliance. By incorporating insulation resistance testing, contact resistance analysis, thermal imaging, and power quality assessments, engineers can prevent failures and enhance switchgear performance.
Proactive maintenance, including tightness checks and visual inspections, ensures that switchgear systems remain in optimal working condition, reducing downtime and improving overall electrical safety.
slot gacor
slot gacor
situs cantiktoto
olympus super scatter
toto macau
slot gacor 4d
situs toto slot
slot gacor
totoagung2
situs toto
bandar togel online
slot gacor 4d
toto slot
totokita3
toto slot
situs toto
situs toto
pay4d
slot gacor maxwin